What is dns settings?
Accessing and changing DNS settings varies depending on your operating system or device. Have you ever wondered how to type “google.com” into your browser and instantly access the world’s most popular search engine? It’s all thanks to a behind-the-scenes hero called the Domain Name System (DNS).
DNS settings act as the internet’s address book, translating user-friendly domain names like “facebook.com” into numerical IP addresses that computers can understand.
In this blog post, we’ll break down DNS settings clearly and concisely, even for those who aren’t tech-savvy.
Buying a domain is an important issue for the website. To buy a domain name permanently select a lifetime registration option with a reputable registrar.
What is DNS?
Ever wondered how you type in a website address like “google.com” and magically land on the right page? It’s all thanks to a clever system called the Domain Name System (DNS), which acts like the internet’s phonebook.
How does DNS work?
DNS works behind the scenes, making the internet easy to navigate for everyone. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how DNS works:
- You Enter a Domain Name: You type a website address (e.g., wikipedia.org) into your browser.
- Your Device Queries a DNS Resolver: Your device’s operating system or internet service provider (ISP) has preconfigured DNS resolver settings. These act like the initial lookups in a phonebook directory.
- The DNS Resolver Takes Action: The DNS resolver checks its local cache (a temporary storage of recently looked-up addresses) to see if it already knows the IP address for wikipedia.org.
- Cache Hit (Fast): If the address is found in the cache, your device can connect to the website immediately.
- Cache Miss (Slower): If the address isn’t in the cache, the resolver sends a query to a series of DNS servers.
- Root Nameservers: The query first goes to root nameservers, which act like the root directory of the phonebook, pointing to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) nameserver (e.g., .org, .com).
- TLD Nameserver: The TLD nameserver directs the query to the authoritative nameservers for the specific domain (wikipedia.org).
- Authoritative Nameservers: These are the servers managed by the website owner, containing the actual IP address linked to wikipedia.org.
- IP Address Returned: The authoritative nameserver sends the IP address for wikipedia.org back to your device’s DNS resolver.
- Connection Established: The DNS resolver receives the IP address and guides your device to connect to the website
What are DNS Settings?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It’s a hierarchical network of servers that translates domain names (like google.com or facebook.com) into numerical IP addresses (like 172.217.160.133 for Google). Think of it like this:
- Domain names are the easy-to-remember website addresses you type into your browser.
- IP addresses are the unique numerical codes assigned to each device on the internet, like a house address.
- DNS settings act as the lookup service, allowing your computer or device to find the correct IP address for a website you want to visit.
Why Should You Care About DNS Settings?
While the DNS works seamlessly in the background most of the time, there are situations where understanding DNS settings can be beneficial:
- Troubleshooting website access issues: If you’re facing trouble accessing a website, it might be due to DNS problems. By knowing how to change your DNS settings, you can try using a different DNS server, which can sometimes resolve the issue.
- Improving website loading speed: Different DNS servers can have varying speeds. If you’re concerned about website loading times, you can experiment with different DNS providers to see if it makes a difference.
- Enhancing security: Some DNS providers offer security features like parental controls or protection from malicious websites. Knowing your DNS settings allows you to explore these options if desired.
- Managing your domain name: If you own a website, you’ll need to manage your DNS settings to point your domain name to the server where your website is hosted.
How DNS Settings
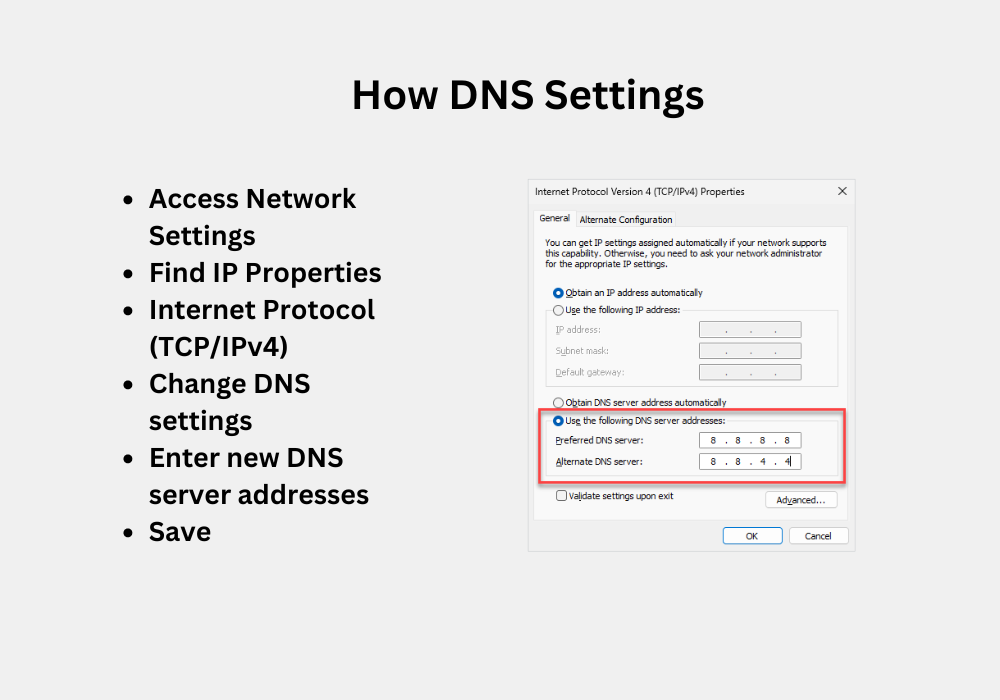
Here’s a simple guide to change them (steps may vary slightly):
- Access Network Settings: Go to your Wifi settings or Network Connections on your device.
- Find IP Properties: Locate your current network connection and find its “Properties” option.
- Internet Protocol (TCP/IPv4): Look for “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and choose “Properties”.
- Change DNS settings: There might be an option like “Obtain DNS server address automatically”. If you want to change it, choose “Use the following DNS server addresses” instead.
- Enter new DNS server addresses: Here, you can enter preferred and alternate DNS server addresses. Popular options include Google’s Public DNS: 8.8.8.8 (preferred) and 8.8.4.4 (alternate).
- Save: Click “Save” or “OK” to apply the new settings.
Remember, these are general steps. Consulting your device’s manual or a quick online search can provide more specific instructions for your device.
How to Find Your DNS Settings:
The process for finding your DNS settings varies depending on your operating system and device. Here’s a general guideline:
- Windows: Go to “Network Connections” > Right-click on your active network connection and select “Properties” > Double-click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” > Look for the “Preferred DNS server” and “Alternate DNS server” fields.
- Mac: Open “System Preferences” > Go to “Network” > Select your active network connection > Click on “Advanced” > Go to the “DNS” tab. Here you’ll see the list of DNS servers your device is using.
- Router: You can also access your router’s settings to configure DNS settings for your entire network. Consult your router’s manual for specific instructions.
Popular DNS Providers
If you’re considering changing your DNS settings, here are some popular and reliable options:
- Google Public DNS: [8.8.8.8] & [8.8.4.4]
- OpenDNS: [208.67.222.222] & [208.67.220.220]
- Cloudflare DNS: [1.1.1.1] & [1.0.0.1]
In Conclusion
Understanding DNS settings empowers you to troubleshoot internet issues, potentially improve website loading times, and explore options for enhanced security or parental controls. By demystifying this essential internet service, you can navigate the online world with a bit more confidence!







