How to Find the Publication Date of a Website
The publication date of a website is often crucial for verifying the accuracy and relevance of its content. Knowing how to find the publication date can be immensely helpful, whether you’re citing sources, doing research, or just curious about when the information was posted. In this blog, we’ll explore easy and effective ways to determine the publication date of a webpage.
Before diving into this blog, check out our previous post on What are Plugins and How Does it Work? It helps you understand What a is Plugin.
Why is the Publication Date Important?
The publication date provides context for the content’s reliability. In rapidly changing fields like technology, medicine, or current events, outdated information might not be trustworthy. Knowing when a webpage was published can help you:
- Ensure the content is current and relevant.
- Evaluate the credibility of the information.
- Properly cite the source in academic or professional work.
Methods to Find Publication Date of a Website

Check for a Visible Date on the Page
The simplest way to find the publication date is to look for it directly on the webpage. Authors or publishers often include this information at the top or bottom of an article. Here are common places where dates appear:
- Below the headline
- Above or below the author’s name
- At the bottom of the article
If the content has been updated, you may also find an “Updated On” or “Last Modified” date near the original publication date.
Inspect the URL for Date Information

Some websites include the publication date in the URL structure. For instance, blogs and news sites often use formats like:
If the URL contains a date, it’s a reliable indicator of when the page was originally published.
Use the Page Source Code
When the date is not visible, checking the page’s HTML source code can help. Here’s how you can do this:
- Right-click anywhere on the webpage and select View Page Source or Inspect.
- Use the search function (Ctrl+F or Command+F) and look for terms like:
- datePublished
- publishDate
- article:published_time
These meta tags often contain the publication date in a format like YYYY-MM-DD.
Check the Sitemap
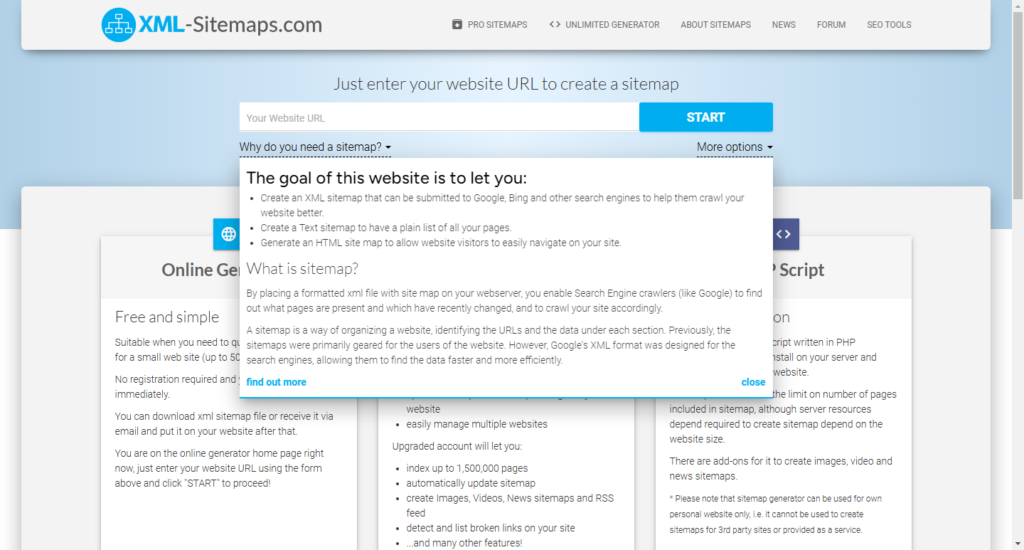
Websites often have an XML sitemap, which lists all the pages along with their publication or last modified dates. To find the sitemap:
- Add /sitemap.xml to the website’s URL (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap.xml).
- Open the file to look for the page’s URL and corresponding date.
Use Online Tools
If manual methods fail, online tools can assist you in finding the publication date. Some useful tools include:
- Wayback Machine (archive.org): This tool provides a history of when a webpage was first indexed. While it may not show the exact publication date, it can give a close approximation.
- SEO Analyzer Tools: Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog often display the publication date of a webpage as part of their analysis.
Search the Website’s Social Media Posts
Businesses and content creators often share new posts or articles on their social media accounts. Searching for the webpage link or title on platforms like Twitter or Facebook might lead you to a post announcing the publication date.
Contact the Website Administrator
If all else fails, consider reaching out to the website’s administrator. Many websites have a “Contact Us” page or provide an email address for inquiries. A polite request for the publication date might yield a quick response.
Why Knowing the Publication Date Matters
Understanding when content was published is essential for several reasons:
- Relevance: Ensures the information is up-to-date.
- Credibility: Demonstrates whether the website maintains current and accurate information.
- Academic Integrity: Citing the publication date is crucial for academic and professional work.
Conclusion
Finding the publication date of a webpage is an essential skill for anyone seeking reliable and current information. By following the methods outlined above, you can often determine the publication date with ease. Remember, if one approach doesn’t work, try another. Eventually, you’ll get the information you need.
Stay informed, and ensure that the content you rely on is both credible and timely!